As electric vehicles (EVs) gain momentum in the automotive market, the importance of robust EV infrastructure becomes undeniable. Charging stations are popping up across cities and highways, making it easier for drivers to transition from traditional gas-powered vehicles to eco-friendly alternatives. This shift not only supports sustainability but also drives innovation in energy consumption and urban planning.
However, the growth of EV infrastructure isn’t without its challenges. From ensuring accessibility to integrating renewable energy sources, stakeholders must navigate a complex landscape to build a reliable network. Understanding the current state of EV infrastructure and its future potential is crucial for consumers, businesses, and policymakers alike. This article explores the key components and developments shaping the EV landscape today.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of EV Infrastructure
EV infrastructure encompasses the essential components that support electric vehicle operation. This includes charging stations, power supply systems, and the integration of renewable energy sources. As demand for EVs rises, the need for a resilient and comprehensive infrastructure becomes critical.
Charging Stations
Charging stations serve as the backbone of EV infrastructure. Over 100,000 public charging stations exist across the United States, facilitating convenient access for EV users. These stations vary in type, from Level 1 chargers that deliver slow charging to Level 3 DC fast chargers that provide rapid energy replenishment. Major cities and highways are prioritized for installation to enhance accessibility.
Power Supply Systems
Power supply systems play a crucial role in driving the transition to electric vehicles. They’re designed to manage energy distribution efficiently and support peak demand periods. Utilities are adopting smart grid technology to optimize electricity flow and integrate renewable energy sources. This integration enhances sustainability and reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Renewable Energy Integration
Integrating renewable energy sources into the EV infrastructure addresses environmental concerns. Solar panels and wind turbines can supply clean energy for charging stations, reducing the carbon footprint of EV charging. Many organizations are investing in energy storage systems to ensure a stable power supply during high-demand times.
Accessibility Challenges
Accessibility remains a significant challenge within EV infrastructure development. Rural areas often lack sufficient charging infrastructure compared to urban regions. Efforts are underway to bridge this gap by expanding charging networks, ensuring all communities can benefit from electric vehicles.
Policy and Investment
Policy and investment drive the evolution of EV infrastructure. Government incentives and funding programs encourage the expansion of charging networks. Initiatives at local and federal levels promote the installation of charging stations, creating an environment conducive to growth in the EV market.
The ongoing advancements in EV infrastructure reflect a commitment to a sustainable future while addressing the challenges inherent in this transition.
Key Components of EV Infrastructure
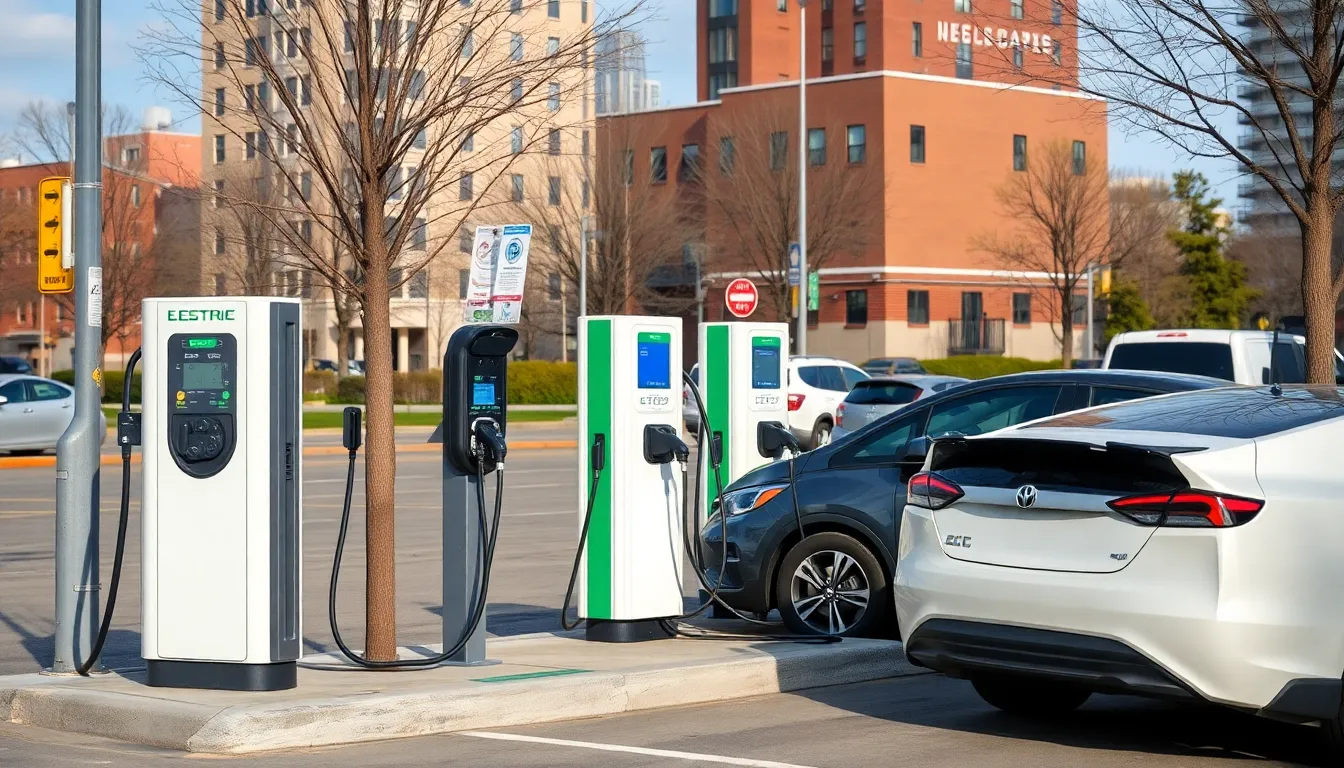
The key components of EV infrastructure include charging stations, power supply systems, and maintenance and service facilities. Each element plays a vital role in supporting the growing network for electric vehicles.
Charging Stations
Charging stations facilitate the electric vehicle transition by providing necessary refueling options. As of 2023, the U.S. hosts over 100,000 public charging stations, categorized into Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast chargers. Level 1 chargers supply 120 volts and are suitable for home use, offering slow charging. Level 2 chargers, utilizing 240 volts, enhance charging speed and are commonly found in commercial and public settings. DC fast chargers deliver over 400 volts, allowing for rapid recharging, crucial for long-distance travel. Strategic placement of these stations along highways and urban centers improves accessibility and convenience for users.
Power Supply Systems
Power supply systems are essential for managing energy distribution to charging stations. These systems ensure reliability during peak demand periods. Utilities incorporate smart grid technology to optimize electricity flow, which includes monitoring and adjusting energy consumption in real time. This adjustment is crucial for integrating renewable energy sources, like solar and wind, with the grid. By employing effective management strategies, power supply systems contribute significantly to the sustainability of EV infrastructure and help reduce the overall carbon footprint.
Maintenance and Service Facilities
Maintenance and service facilities ensure the longevity and efficiency of charging equipment. Regular maintenance of charging stations minimizes downtime and maximizes reliability for users. These facilities also support technicians in troubleshooting and repairing equipment, ensuring that all components of the infrastructure function optimally. Incorporating advanced diagnostic tools enables quicker service responses, enhancing user satisfaction and supporting the growing demand for electric vehicle charging services.
Benefits of Robust EV Infrastructure
Robust electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure offers significant advantages that contribute to environmental sustainability and economic progress. These benefits extend across various sectors and enhance the overall adoption of electric vehicles.
Environmental Impact
Environmental impact improves with expanded EV infrastructure. The integration of charging stations directly correlates with a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Studies show that EVs produce 50% fewer emissions than conventional vehicles. Enhanced charging networks support the transition to renewable energy sources by accommodating solar and wind power, further decreasing the carbon footprint associated with EV charging. Efficient charging facilities encourage more users to switch to electric vehicles, ultimately leading to cleaner urban air and a decrease in dependency on fossil fuels.
Economic Growth
Economic growth flourishes with the development of robust EV infrastructure. The expansion of charging stations creates job opportunities in installation, maintenance, and management of charging facilities. According to the International Labor Organization, the electric vehicle sector can generate 10 million jobs globally by 2030. Investment in EV infrastructure stimulates local economies, as businesses can attract more customers with accessible charging options. Furthermore, addressing the demand for charging stations influences technology innovation, which leads to advancements in battery efficiency and vehicle design, driving overall economic performance.
Challenges and Opportunities
The expansion of electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure faces significant challenges but also presents numerous opportunities for growth and improvement. Understanding these factors is crucial for maximizing the potential of EV technology.
Technological Barriers
Technological barriers hinder the rapid development of EV infrastructure. Insufficient charging speeds can deter users; Level 1 chargers may take up to 24 hours for a full charge, while DC fast chargers provide quicker solutions, taking about 30 to 45 minutes. Inconsistent infrastructure quality across locations leads to user frustration. Compatibility issues between various EV models and charging stations pose further challenges, requiring standardization efforts. Scalability of charging networks remains a concern as the number of EVs increases; estimates suggest a need for over 2 million public charging stations in the U.S. by 2030 to adequately support anticipated demand.
Policy and Regulation
Policy and regulation significantly impact EV infrastructure development. Inconsistent regulatory frameworks at the local, state, and federal levels create confusion and slow deployment. Incentives and funding from government initiatives play a crucial role in accelerating infrastructure growth. For instance, the federal government allocated $7.5 billion for EV charging station expansion in 2021. Streamlined permitting processes can facilitate quicker installation, while policies promoting renewable energy integration enhance the environmental benefits of charging stations. Ongoing collaboration among stakeholders, including government bodies, utility companies, and private enterprises, can lead to comprehensive frameworks that support sustainable infrastructure development.
Future Trends in EV Infrastructure
Innovations and developments in EV infrastructure are shaping the future, enhancing connectivity, and improving user experience. As technology advances, the EV landscape continues to evolve rapidly.
Innovations and Developments
Innovations play a pivotal role in the enhancement of EV infrastructure. Smart charging solutions introduce features like demand response, enabling charging systems to adjust to grid conditions and user preferences. Wireless charging technology, still in early adoption phases, offers potential for convenience without physical connections. Furthermore, integrated payment systems simplify the charging process, allowing users to seamlessly pay via mobile apps.
Another notable development involves vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology. V2G systems permit two-way energy flow, allowing EVs not only to draw power but also to feed energy back into the grid during peak demand. This reduces strain on power resources and promotes renewable energy use, optimizing overall energy efficiency.
Global Adoption Rates
Global adoption rates of EV infrastructure demonstrate a significant upward trajectory. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global EV stock reached over 10 million units in 2020, a clear indication of growing acceptance. The U.S. has seen a 40% increase in new electric vehicle registrations from 2020 to 2021, reflecting a robust shift towards electrification.
China leads in EV adoption, accounting for nearly 50% of global sales in 2019. Moreover, Europe shows substantial growth in charging stations, with an approximate 100% increase in public charging points reported from 2018 to 2021. Investments in charging infrastructure and supportive policies across various nations contribute significantly to this trend. The global commitment to reducing emissions aligns with the rapid expansion of EV infrastructure, promoting a cleaner, sustainable future.
The evolution of EV infrastructure is crucial for the future of transportation and environmental sustainability. As the demand for electric vehicles continues to rise, so does the need for an extensive and reliable charging network. This infrastructure not only supports the transition to cleaner energy but also fosters economic growth through job creation and technological innovation.
Addressing the challenges of accessibility and inconsistent infrastructure quality will be vital in ensuring that all communities can benefit from electric vehicles. With ongoing investments and advancements in smart technologies, the path towards a sustainable future is becoming clearer. The commitment to enhancing EV infrastructure reflects a collective effort to reduce emissions and promote a cleaner planet for generations to come.




